Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Insulin Release, 2022
Acknowledgement: David S. Goodsell, RCSB Protein Data Bank and Scripps Research. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-044
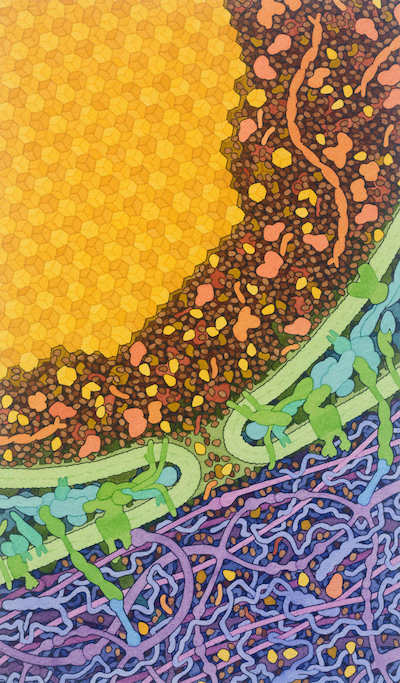
This painting depicts one of the few examples of a protein crystal with a biological function. Insulin is stored in pancreatic beta cells in the form of small crystals, carried inside specialized vesicles. When insulin is needed after meals, these vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and the crystals dissolve, releasing insulin into the bloodstream. The painting shows the vesicle in the process of releasing insulin. The insulin crystal is at the top in yellow, the fused vesicle membrane and cell membrane are in green, and the extracellular matrix that surrounds the beta cell is at bottom in tans and browns.
The painting was created as part of the SciArt Show held at the 2022 meeting of the American Crystallographic Society.