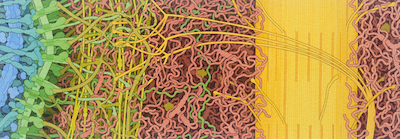
Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Collagen and Extracellular Matrix, 2021
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell, RCSB Protein Data Bank. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-033
A network of fibrous proteins and polysaccharides form a structural matrix between cells in our bodies. In this cross section, a cell surface is at left. A dense basal lamina braces the outside of the cell, composed on long collagen fibers, cross-shaped laminin proteins, and snaky proteoglycan molecules. Other forms of collagen help to strengthen the extracellular matrix, including huge collagen structural fibrils (at right in yellow) and anchoring fibrils (arching molecules in yellow). This painting was created as part of the celebration of the 50th anniversary of the Protein Data Bank, and is adapted from Figure 6.3 of "The Machinery of Life".