Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Casein Micelle and Fat Globule in Milk, 2021
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell, RCSB Protein Data Bank. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-039
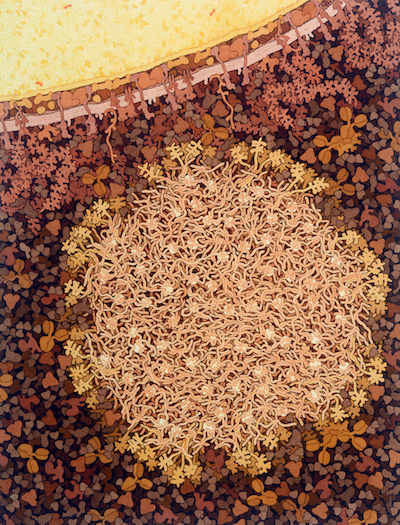
This illustration shows a cross section through a casein micelle (tan, lower center) and a fat globule (yellow, upper left) from cow's milk. The micelle includes many unstructured alpha and beta casein chains interacting with small calcium phosphate nanoclusters (white), and kappa casein chains extending from the surface. The fat globule is surrounded by a multi-layered membrane with many embedded proteins, filled with fat molecules (yellow) and a few carotene molecules (orange). Whey proteins are shown in darker shades around the micelle.
This illustration was presented as part of the Molecule of the Month on Casein Kinase.
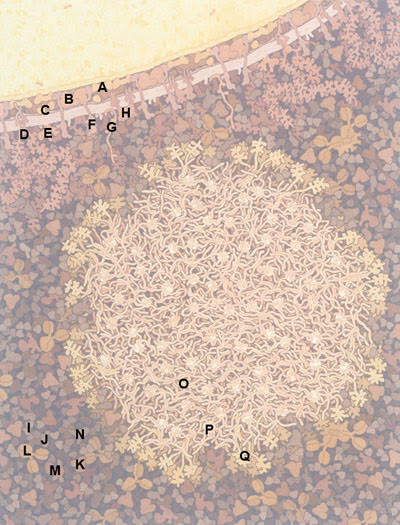
Fat globule membrane
A. Adipophilin
B. Xanthine oxidase
C. Fatty-acid-binding protein
D. Mucin
E. Lactadherin
F. Butyrophilin
G. Proteose peptone
H. CD36
Whey
I. β-Lactoglobulin
J. α-Lactalbumin
K. Albumin
L. Immunoglobulin
M. Lactoferrin
N. Lactoperoxidase
Casein micelle
O. α/β-Caseins
P. Calcium phosphate nanocluster
Q. κ-Casein
Selected References
Roy D, Ye A, Moughan PJ, Singh H (2020) Composition, structure, and digestive dynamics of milk from different species--a review. Front. Nutrition 7, 577759.
de Kruif CG, Huppertz T, Urban VS, Petukhov AV (2012) Casein micelles and their internal structure. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 171-172, 36-52.
Lopez C (2011) Milk fat globules enveloped by their biological membrane: unique colloidal assemblies with a specific composition and structure. Curr. Op. Colloid Interf. Sci. 16, 391-404.
McMahon DJ, Oommen BS (2008) Supramolecular structure of the casein micelle. J. Dairy Sci. 91, 1709-1721.
Madureira AR, Pereira CI, Gomes AMP, Pintado ME, Malcata FX (2007) Bovine whey proteins--overview on their main biological properties. Food Res. Internat. 40, 1197-1211.




