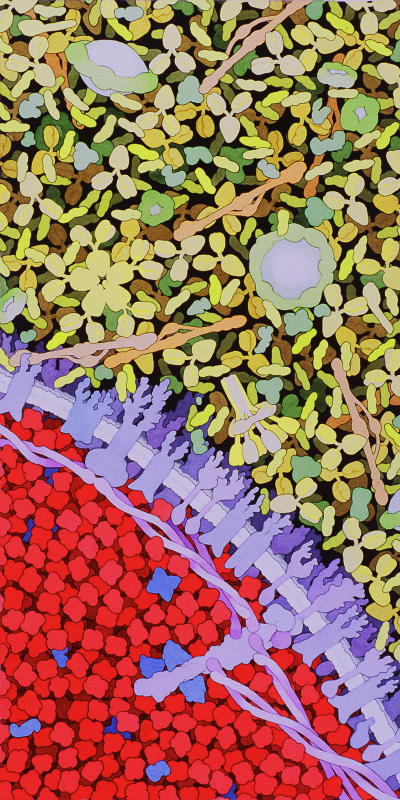
Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Blood, 2000
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell, The Scripps Research Institute. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-003
This illustration shows a cross-section through the blood, with blood serum in the upper half and a red blood cell in the lower half. In the serum, look for Y-shaped antibodies, long thin fibrinogen molecules (in light red) and many small albumin proteins. The large UFO-shaped objects are low density lipoprotein and the six-armed protein is complement C1. The red blood cell is filled with hemoglobin, in red. The cell membrane, in purple, is braced on the inner surface by long spectrin chains connected at one end to a small segment of actin filament.